Tempco is participating in the project for the European project ELSMOR (European Licensing of Small MOdular Reactors) experimental nuclear plant with the supply of a plate heat exchanger (S-CSG, Safety-Compact Steam Generator) employed as a device for passive decay heat removal in case of nuclear reactor fault.
This is the first plant in the world developed using a plate heat exchanger for the emergency cooling system that works by natural convection circulation, therefore without pumps or the need of electricity, to cool the reactor while it turns safe. The exchanger is therefore a key component of the Decay Heat Removal System (DHRS) of the ELSMOR project, as part of the experimental campaign carried out at SIET, described in detail in this article.
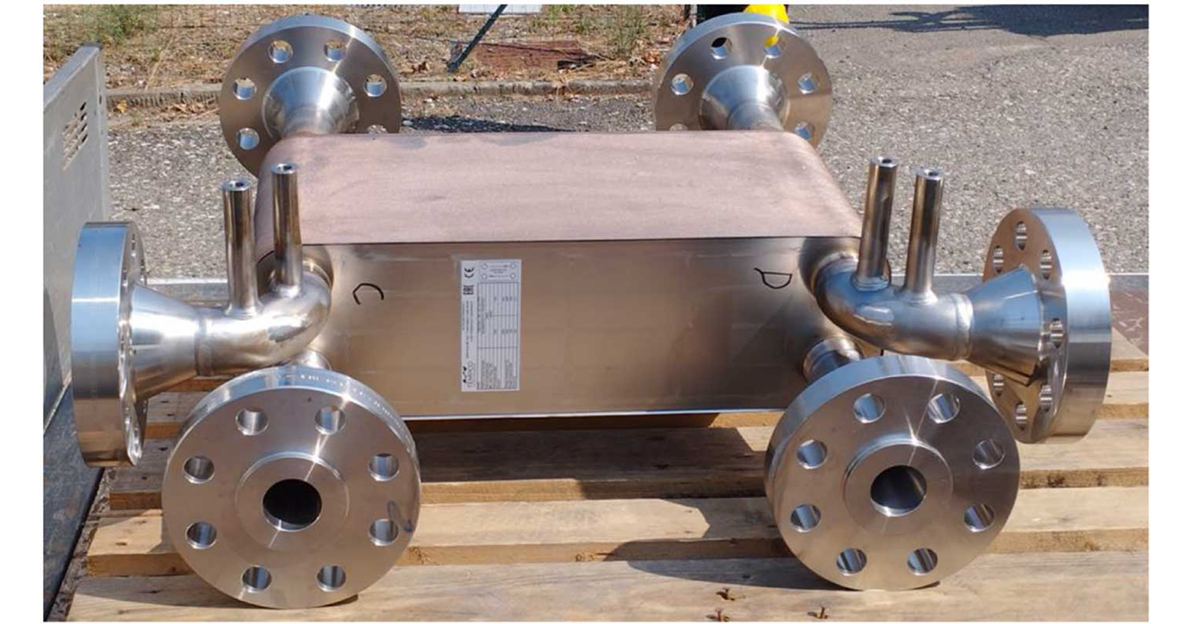
S-CSG plate heat exchanger before installation
The exchanger supplied by Tempco is a compact, high-efficiency type that uses corrugated plates to maximize the heat transfer surface. The S-CSG specifically acts as an interface between the primary circuit (reactor side) and the secondary circuit (natural side with dissipation in a water pool) of the DHRS system. The hot fluid of the primary circuit then transfers its heat to the fluid of the secondary circuit through the plates of the exchanger. The secondary fluid, in turn, dissipates heat into the water pool through another heat exchanger.
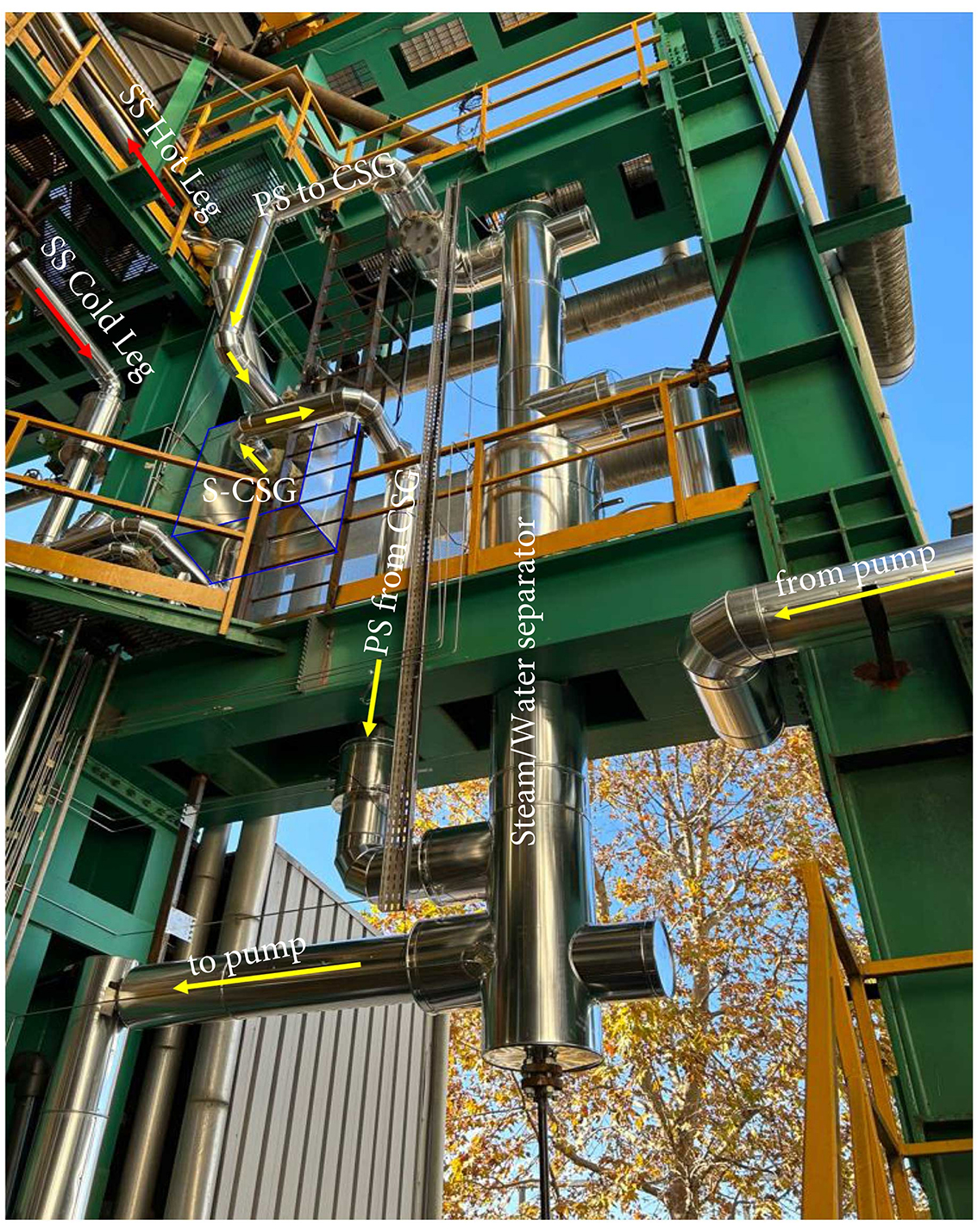

View of primary side of ELSMOR plant and S-CSG
The S-CSG is therefore a fundamental component for the safety of the reactor in case of an accident. In the event of a coolant loss, the S-CSG can remove waste heat from the reactor and prevent overheating.
The plate exchanger in the system offers a number of advantages:
- High heat exchange efficiency
- Compact dimensions
- Easy maintenance
- Low cost
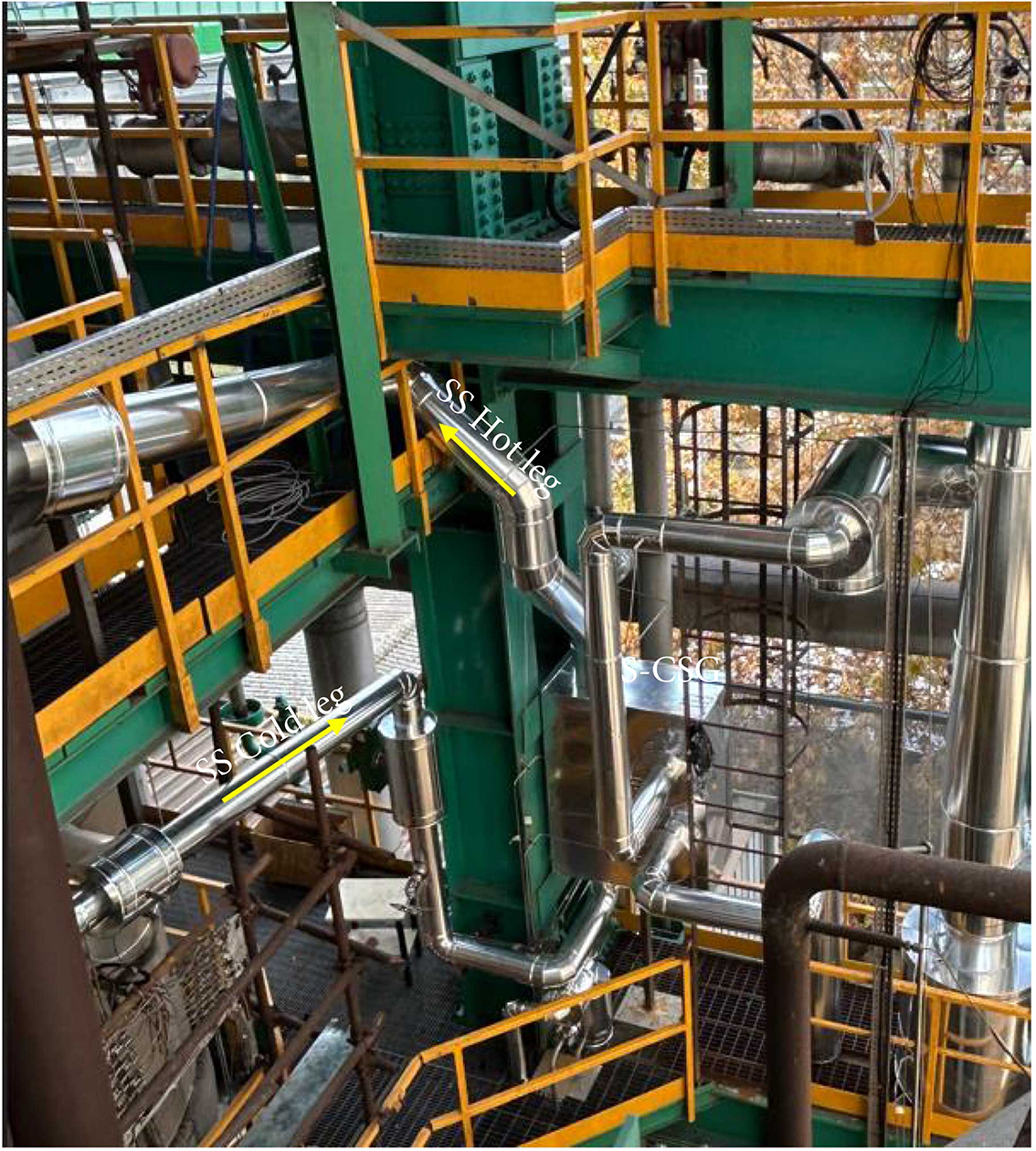

View of secondary side of ELSMOR plant and S-CSG
The tests conducted on the ELSMOR system therefore demonstrates the effectiveness of the S-CSG in removing waste heat. The results showed that the exchanger is capable of operating stably under a wide range of operating conditions.
A key element of the DHRS system of the ELSMOR project, the heat exchanger therefore proves itself to be an ideal choice for the removal of decay heat from nuclear reactors thanks to its efficiency, reliability and compactness. For the prototype plant, which served for the characterization and testing of the system, a TCB exchanger was supplied, a solution that clearly will not be possible to use in the executive phase. Through the next developments of the project, for the specific application we will study a special dedicated plate heat exchanger, which could be a PCHE (Printed circuit heat exchanger) type.
